Behaviour of Real Gases
Behaviour of Real Gases: Overview
This topic covers concepts such as Real Gas, Deviations from Ideal Gas Behaviour, Compressibility of Gas, Compressibility Factor, Variation of Compressibility Factor with Temperature, Variation of Compressibility Factor with Pressure, etc.
Important Questions on Behaviour of Real Gases
The pressure exerted by 1 mole of CO2 at 273 K, is 34.98 atm. Assuming that volume occupied by CO2 molecules is negligible, the value of van der Waals' constant for attraction of CO2 gas is :
A gas is said to behave like an ideal gas when relation constant. When do you expect real gas to behave like an ideal gas?
In Van der Waal’s equation of state for a non-ideal gas, the term that accounts for intermolecular forces is:
Van der Waal’s real gas, act as an ideal gas, at which conditions ?
At which one of the following temperature – pressure conditions the deviation of a gas from ideal behaviour is expected to be minimum ?
When deviation is more in the behaviour of a gas from the ideal gas equation PV = nRT ?
The two assumptions of kinetic molecular theory of gases do not hold good at high _____ or low temperature.
Identify the postulate of kinetic molecular theory of gases which does not hold good under all conditions.
Identify the postulate of kinetic molecular theory of gases which does not hold good under all conditions.
Write the postulates of kinetic theory of gases which do not hold good under all the conditions of temperature and pressure.
According to kinetic theory, the gas particles occupy a negligible fraction of the total volume of the gas. This assumption is responsible for the volume correction in the ideal gas equation of real gases.
Mentions two assumptions of kinetic theory of gases, which are responsible for the volume correction in the ideal gas equation of real gases.
Explain the factors responsible for the volume correction in the ideal gas equation of real gases.
The isotherms of a gas are shown below :
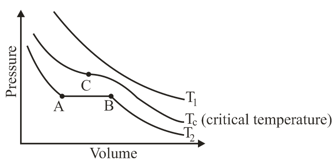
Among the following,
(i) At , the gas cannot be liquefied
(ii) At point , liquid starts to appear at
(ii) is the highest temperature at which the gas can be liquefied
(iv) At point , a small increase in pressure condenses the whole system to a liquid
The correct statements are :
Which of the following expressions is correct between the van der Waals constant and the radius of spherical molecules?
For an ideal gas, the compressibility factor is
For one mole of a van der Waals' gas, the compressibility factor at a fixed volume will certainly decrease, if
[Given : " a " and " b " are standard parameters for van der Waals' gas]
The pressure and volume isotherm of a van der Waals' gas, at the temperature at which it undergoes gas to liquid transition, is correctly represented by
is also called internal _____ of the gas where is a measure of force of attraction between gas molecule.
Which of the following represents a plot of compressibility factor vs pressure at room temperature for
